
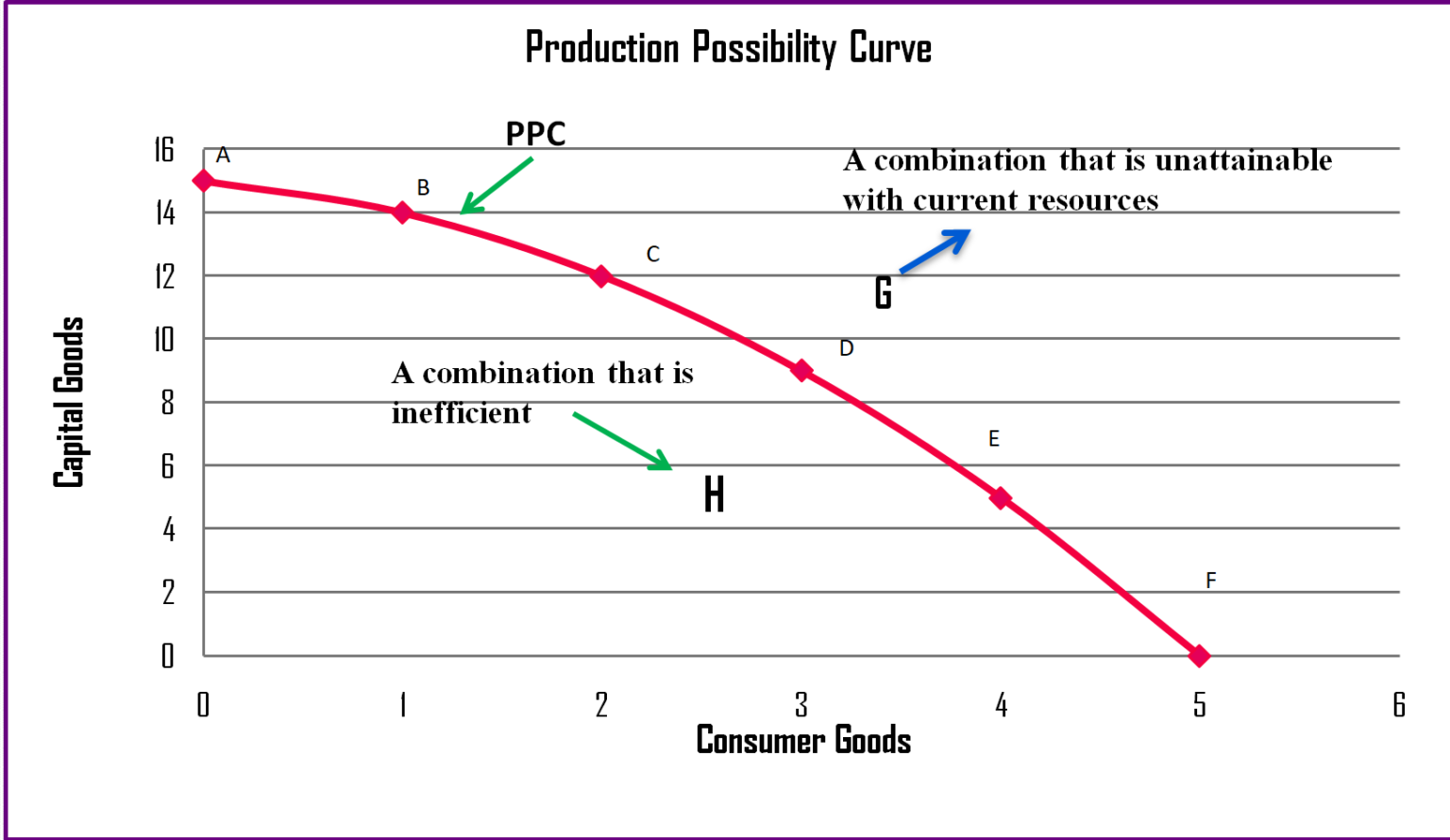
However, putting those marginal dollars into education, which is completely without resources at point A, can produce relatively large gains. Diverting some resources away from A to B causes relatively little reduction in health because the last few marginal dollars going into healthcare services are not producing much additional gain in health. Now imagine that some of these resources are diverted from healthcare to education, so that the economy is at point B instead of point A. People are having cosmetic surgery on every part of their bodies, but no high school or college education exists. For example, children are seeing a doctor every day, whether they are sick or not, but not attending school. This situation would be extreme and even ridiculous. At point A, all available resources are devoted to healthcare and no resources are left for education. The PPC in the figure below has 3 main points: A, B, and C.To understand why the PPF is curved, start by considering point A at the top left-hand side of the PPF. Production possibility curves and economic growth The PPC can be used to explain and understand the macroeconomic environment. Macroeconomic production possibility curve diagrams This is because when there is economic growth, that means more supply resulting from an increase in demand. This is represented in Figure 4 with the shift of the graph Y to Y2. Simultaneously, the LRAS curve also shifts to the LRAS 2 curve on the right, as it is positively affected by economic growth. This is shown in Figure 3 where the graph XY shifts to X2Y2. The negative economic growth could be due to a decrease in production factors, or a decrease in demand, both of which lead to a decrease in supply.Īn outward shift in PPC means economic growth. The PPC shifts inwards as shown in Figure 3, when the graph XY shifts to X1Y1, and the LRAS curve shifts to the LRAS 1 curve on the left, as shown in Figure 4, when the graph Y shifts to Y1. When there is negative economic growth, both the PPC and LRAS curves are negatively affected. The LRAS curve of an economy represents a point on the country’s PPC. This means that when there is a change in the production factors such as the resources, labour capacity, advancements in technology etc., the LRAS curve will change.

Similar to the PPC, the LRAS curve also depends on the factors of production. The shifts in the PPC is linked to the shift of the economy’s Long Run Aggregate Supply curve or LRAS curve. 3 - The shift in the production possibility curve
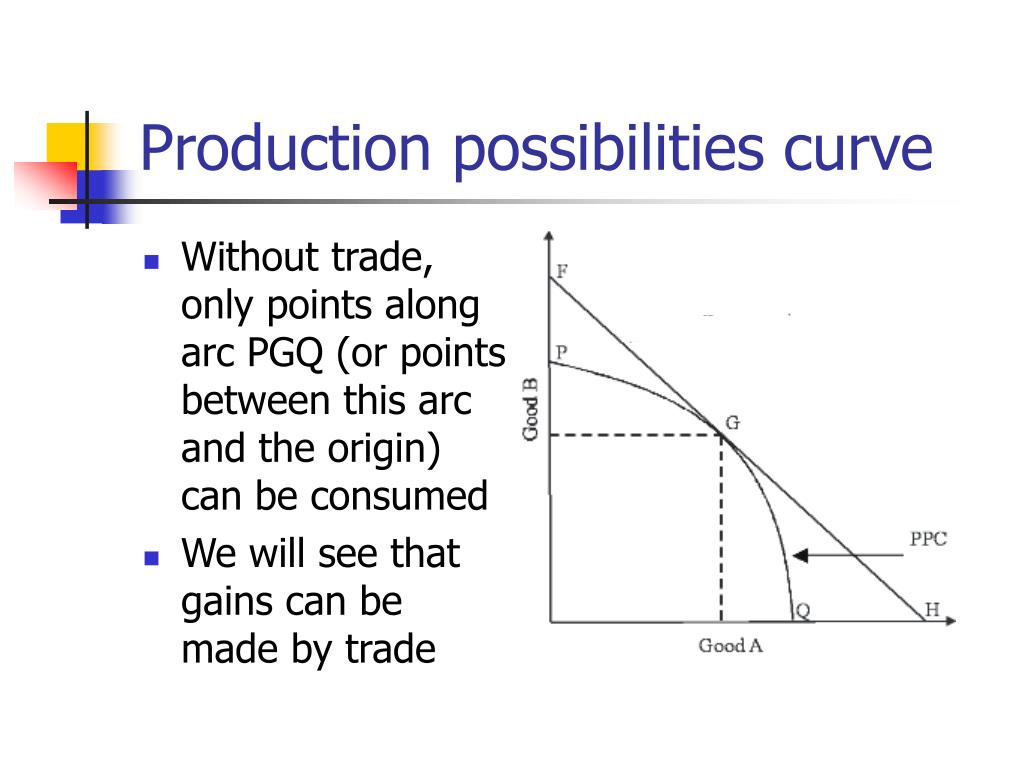
On the flip side, when a factor of production such as capital decreases, the PPC shifts inwards, indicating that the economy is producing fewer quantities.įig. In this situation, the curve, X1Y1, shifts outwards to the curve X 2Y 2. When a factor of production such as capital increases, the PPC shifts outwards, indicating that the economy can produce more. The factors of production are land, labour, capital, and enterprise. Shifting the production possibility curveĪ PPC will shift inwards or outwards when there is a change in the factors of production. To attain these levels the country will have to increase their resources, improve its technology, and productivity. The points above the PPC, such as point Q, are output combinations that are unsustainable at the given time. The points that fall under the curve, such as point P, mean that the resources are either inefficiently employed or are not fully employed. It is important to remember that the production of one product can not be increased without the decrease in the production of another product. Any point on the curve also shows maximum production of products. Points such as A and B on the curve show maximum production that can be achieved by the economy. 2 - Points along the production possibility curve Point Y shows maximum sugar production and minimum wheat production.įig.

In Figure 2, point X shows maximum wheat production and zero sugar production. Price Determination in a Competitive Market.Market Equilibrium Consumer and Producer Surplus.Determinants of Price Elasticity of Demand.Cross Price Elasticity of Demand Formula.Effects of Taxes and Subsidies on Market Structures.Monopolistic Competition in the Short Run.Monopolistic Competition in the Long Run.Behavioural Economics and Public Policy.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
